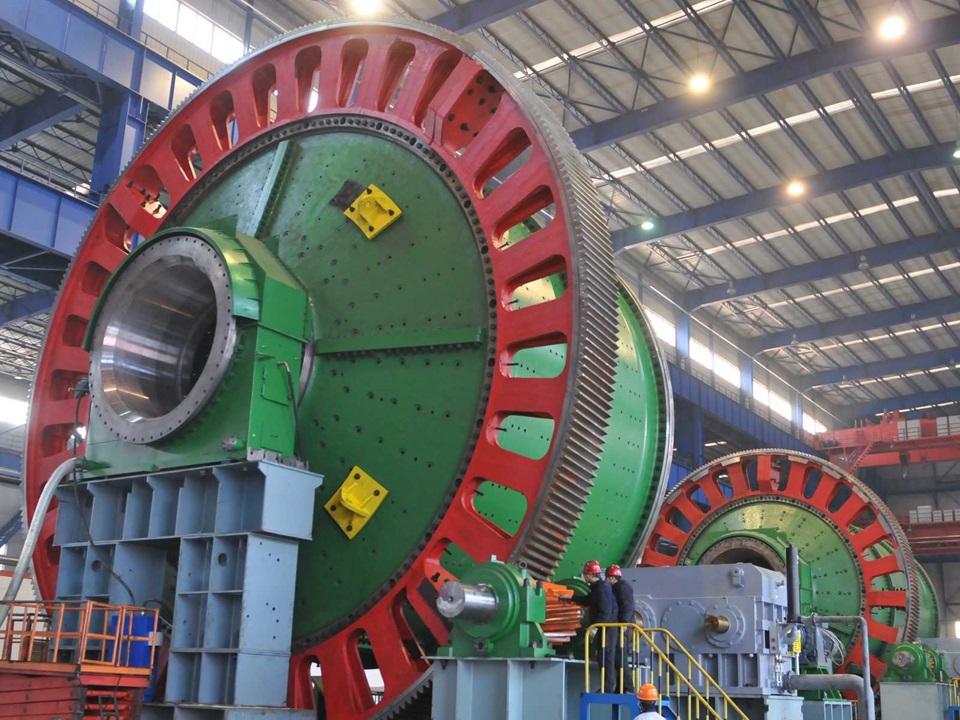
A large ball mill is a strong machine in big factories. It breaks down material into tiny pieces to help with processing. The ball mill has spinning cylinders with grinding media inside. These crush the material. Large ball mills help factories make more products. They are used in places that need fast and good material processing.
Key Takeaways
-
Large ball mills have spinning cylinders and grinding media. They break down materials fast and well. This helps factories make more products. It also helps save energy.
-
Good design is important. Strong shells, liners, and the right grinding media help the ball mill work well. This lets it run for many hours. It can also handle different materials safely.
-
Operators must watch the speed and grinding media amount. They must also follow safety rules. This keeps the ball mill working well and safe. It helps the ball mill last long in many industries.
Large Ball Mill Features
Components
A large ball mill has several main parts. The shell is a strong, round cylinder that holds everything together. Inside the shell, grinding media like steel balls or rods move around. These pieces help break down the material. Liners cover the inside of the shell. They protect the shell from wear and help guide the grinding media. The ball mill also has a motor and gears to spin the shell.
The liners in a ball mill come in different materials. Each type has its own benefits. The table below shows some common liner materials and their uses:
|
Material Type |
Typical Composition (wt%) |
Benefits and Application Context |
|---|---|---|
|
High Manganese Steel |
High Mn content |
Tough and widely used, but can break or bend under stress. |
|
High Chromium Cast Iron |
C 2.2-2.8%, Cr 13-16%, Si 0.5-1.0%, Mn 0.6-1.2%, Mo 0.5-1.3% |
Very good wear resistance, lasts a long time, best for rough grinding. |
|
Medium Carbon Low Alloy Chromium Manganese Steel |
C ~0.38-0.52%, Cr 1.6-2.5%, Si 0.5-1.2%, Mn 1.5-2.4%, Mo 0.2-0.5% |
Good balance of cost and performance, used for fine grinding. |
|
Alloy Steel |
Varies |
Chosen for special needs in strength and wear. |
Design
Engineers design a ball mill to handle large amounts of material. The shell is thick and strong. It can spin at different speeds. The grinding media inside the shell move and hit the material. This action breaks the material into smaller pieces. The liners help keep the grinding media moving in the right way. The design allows the ball mill to work for many hours without stopping.
Grinding Media
Grinding media are the tools that crush the material inside the ball mill. Most ball mills use steel balls, but some use rods or other shapes. The size and type of grinding media depend on the material being processed. The grinding media must be hard and strong. They need to last a long time and not break easily. The ball mill can work in dry or wet modes. In dry mode, the grinding media and material stay dry. In wet mode, water or another liquid helps with the grinding process. This flexibility makes the ball mill a useful type of grinder for many industries.
Ball Milling Process in Industry
Operation
A ball mill works by spinning a big cylinder. The cylinder is filled with grinding media and material. The cylinder turns at a certain speed. Steel balls or rods move inside the mill. They hit the material again and again. This breaks the material into smaller pieces. Factories use this process to make materials smaller. The ball mill can work with dry or wet materials. Operators put in the right amount of material and grinding media. They set the speed for the job. The process goes on until the material is small enough. Workers take out the finished product for the next step.
Efficiency
How well a ball mill works depends on many things. These things help the mill grind material evenly and finely.
-
The way steel balls move inside the cylinder changes how well it grinds. Different paths, like falling or rolling, change impact and wear.
-
The speed of the cylinder is important. Low speed means less impact and slower grinding. High speed gives more impact and crushes better, but only up to a point.
-
The number of steel balls matters. Too few balls do not grind well and cause more wear. Too many balls stop them from moving and waste energy.
-
The size and type of steel balls also matter. Big balls give more impact. Small balls help make finer particles.
-
The amount of material and the type of liner change how the balls move and hit the material.
-
Some factories use grinding agents to help the mill work better.
Operators watch these things closely. They change the process to get the best results. This helps the ball mill turn big pieces into the right size for industry.
Safety
Safety is very important when using a ball mill. Workers must follow rules to stay safe. They wear gloves, goggles, and ear protection. The ball mill has guards and covers to prevent accidents. Operators check the machine before using it. They look for loose parts or damage. Regular care keeps the ball mill working well. Workers clean the mill and change worn liners or grinding media. They also check the motor and gears.
Tip: Always turn off the power before fixing the ball mill.
Factories teach workers what to do in emergencies. They show how to stop the ball mill fast if needed. Good safety steps protect workers and keep the process running well.
Applications and Equipment
Industrial Uses
Large ball mills are important in many industries. Cement factories use them to grind raw materials into powder. Mining companies use ball mills to crush rocks and get minerals. Chemical plants use ball mills to mix and blend materials. Food producers use ball mills to make chocolate and flour. Ceramic factories use ball mills to shape clay and glaze. Each industry needs ball mills to make better products.
Note: Ball mills help companies save time and energy. They make materials easier to process.
Ball Milling Equipment
Ball milling equipment comes in many sizes and shapes. Some mills are small and can sit on a table. Others are very big and fill whole rooms. Engineers pick the right equipment for each job. The equipment has a shell, grinding media, liners, motor, and control system. Good ball milling equipment lasts long and works with many materials. Factories use special equipment for wet or dry grinding.
|
Industry |
Common Ball Mill Use |
|---|---|
|
Cement |
Grinding limestone |
|
Mining |
Crushing ore |
|
Chemicals |
Mixing powders |
|
Food |
Milling grains |
|
Ceramics |
Shaping clay |
Challenges
Factories have some problems with ball mills. The machines need regular care to keep working. Grinding media and liners wear out and must be replaced. Ball mills use a lot of energy, so costs can go up. Dust and noise from ball mills can bother workers. Engineers try to fix these problems and make ball mills safer and better.
A large ball mill helps factories make more products. It also helps save energy for many industries. This machine makes processing materials quick and simple. Experts think new designs and better controls will come soon. People need to look at the good and bad sides before picking a large ball mill for their factory.
FAQ
Q: What materials can large ball mills process?
A: Large ball mills can grind minerals, ores, cement, chemicals, grains, and clay. They work with hard and soft materials in many industries.
Tip: Always check what material you have before using the ball mill.
Q: How often should workers replace grinding media and liners?
A: Factories change grinding media and liners when they get worn out. Most mills need new parts after a few months of heavy work.
-
Regular checks help stop damage.
-
Changing parts keeps the mill safe to use.
Q: Are large ball mills safe for workers?
A: Large ball mills have guards and covers for safety. Workers wear safety gear. Training teaches workers to follow rules and avoid accidents.
Note: Safety training helps lower risks in factories.