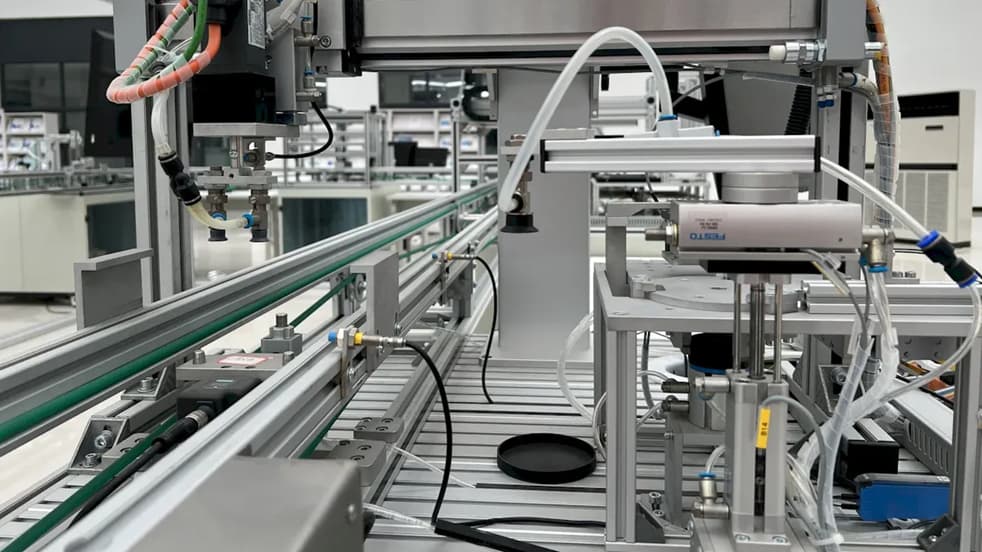
I. Introduction

Angle grinders are versatile power tools that find applications in various industries, construction sites, and DIY projects. Choosing the right angle grinder can significantly impact the efficiency and ease of your work. One of the key decisions when selecting an angle grinder is whether to opt for a corded or cordless model. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the differences between corded and cordless angle grinders, highlighting their respective advantages, limitations, and considerations to help you make an informed choice. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of which type of angle grinder best suits your specific needs and projects.
II. Understanding Corded Angle Grinders
Operational Mechanism
Corded angle grinders are powered directly from an electrical outlet using a power cord. This direct connection ensures a consistent power supply, which can be advantageous for prolonged or heavy-duty tasks that require uninterrupted operation.
Advantages of Corded Angle Grinders
Constant Power: Corded angle grinders provide a continuous power source, allowing for consistent performance without the need for recharging or battery replacements.
Unlimited Runtime: With a corded model, you can work for extended periods without interruption, making them ideal for tasks that demand continuous operation.
Limitations of Corded Angle Grinders
Restricted Mobility: The power cord limits the mobility of corded angle grinders, requiring the user to be near a power outlet. This constraint can be cumbersome, especially in larger workspaces or outdoor settings.
Dependency on Power Outlets: Corded angle grinders rely on the availability of power outlets, which may not always be convenient or accessible in all work environments.
Performance Considerations
Power Output: Corded angle grinders typically deliver higher power output compared to their cordless counterparts, making them suitable for heavy-duty cutting, grinding, and shaping tasks.
Consistent Speed: The direct electrical connection ensures a stable speed and performance level throughout the operation, enhancing precision and efficiency.
Safety Precautions
Electrical Safety: Users of corded angle grinders must be cautious of the power cord to prevent tripping hazards and ensure safe operation around electrical outlets.
Grounding Requirements: Proper grounding of the tool is essential to prevent electrical hazards and ensure user safety when using corded angle grinders.
III. Exploring Cordless Angle Grinders
Functionality of Cordless Angle Grinders
Cordless angle grinders operate using rechargeable batteries instead of being directly connected to a power source. This design offers greater mobility and flexibility compared to corded models.
Advantages of Cordless Angle Grinders
Portability: Cordless angle grinders are highly portable, allowing users to move freely without being restricted by a power cord. This feature is particularly beneficial for tasks in remote locations or areas without easy access to power outlets.
Freedom of Movement: The absence of a cord enables users to work in tight spaces or at awkward angles more comfortably, enhancing overall maneuverability during various applications.
Limitations of Cordless Angle Grinders
Limited Runtime: Cordless angle grinders have a finite runtime based on the battery capacity, which may require recharging or battery replacements during extended use. Users need to consider the battery life when planning for longer tasks.
Recharging Requirement: Recharging the batteries of cordless angle grinders is necessary to maintain their functionality, which can lead to downtime if the batteries run out mid-task.
Performance Factors
Battery Life: The runtime of cordless angle grinders depends on the battery capacity and the intensity of the task. Higher capacity batteries offer longer operating times before requiring recharging.
Portability vs. Power: Cordless models provide portability but may have slightly lower power output compared to corded versions. Users should balance mobility needs with the power required for their specific applications.
User Convenience:
Ease of Use: Cordless angle grinders are user-friendly and do not have the limitations of a power cord, allowing for more flexible and comfortable operation.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of batteries is essential to ensure optimal performance. Users should follow manufacturer guidelines for battery care and charging practices.
IV. Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Corded and Cordless Angle Grinders
Project Requirements:
Intensity and Duration of Use: Consider the nature of your projects. For heavy-duty tasks that require continuous operation, a corded angle grinder with consistent power may be more suitable. For occasional and short tasks, a cordless model might suffice.
Mobility Needs: Evaluate whether you require the freedom of movement that a cordless angle grinder provides or if you can work effectively within the reach of a power outlet with a corded tool.
Budget Considerations
Initial Investment: Corded angle grinders typically have a lower initial cost compared to cordless models, as they do not come with the added expense of batteries and chargers. Consider your budget constraints when making a purchase decision.
Long-Term Costs: While cordless angle grinders may have a higher upfront cost, assess the long-term operating costs, including battery replacements and maintenance, to determine the overall cost-effectiveness of each option.
User Preferences
Comfort with Tool Type: Some users may prefer the convenience and portability of cordless angle grinders, while others may prioritize the consistent power supply of corded models. Choose based on your comfort level and familiarity with each type of tool.
Experience with Battery-Operated Tools: If you have experience using battery-operated tools and are comfortable with managing battery life and recharging, a cordless angle grinder may be a suitable choice.
Task Specificity
Precision and Power Requirements: Evaluate the power output needed for your tasks. Corded angle grinders typically offer higher power levels, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that demand more torque and cutting power.
Flexibility and Maneuverability: If your projects involve working in confined spaces or require frequent tool movement, a cordless angle grinder's portability and freedom of movement may be advantageous.
Future Expansion and Versatility
Compatibility with Existing Tools: Consider whether your choice aligns with your existing tool collection and future expansion plans. Opt for a tool that complements your workflow and enhances overall productivity.
Versatility Across Applications: Assess how well the selected angle grinder can adapt to various applications and projects, ensuring versatility and efficiency in different work settings.
V.Conclusion
Selecting the right angle grinder, whether corded or cordless, is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and success of your projects. In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the key differences between corded and cordless angle grinders, highlighting their respective advantages, limitations, and factors to consider.
When making your decision, it is essential to assess your project requirements, budget constraints, user preferences, and task specificity. Consider the intensity and duration of your tasks, the need for mobility, and the power output required for optimal performance. Balance these factors with your comfort level and familiarity with each type of tool to make a choice that aligns with your needs.
Ultimately, the choice between a corded and cordless angle grinder boils down to finding the tool that best suits your working style, project demands, and long-term goals. Whether you prioritize consistent power supply and high performance with a corded model or value mobility and flexibility with a cordless option, ensure that your decision enhances your workflow and productivity.
By carefully evaluating these factors and considerations, you can confidently choose the right angle grinder that empowers you to tackle tasks efficiently and effectively. Remember to prioritize safety, maintenance, and proper usage practices to maximize the longevity and performance of your chosen tool. Make an informed decision based on your unique requirements, and let your angle grinder be a valuable asset in your workshop or project endeavors.