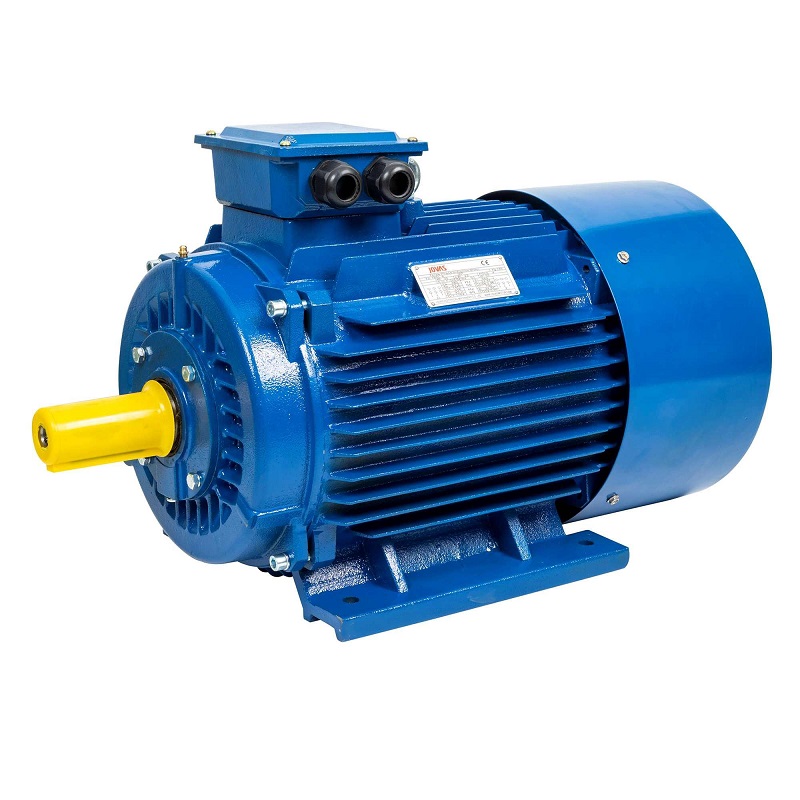
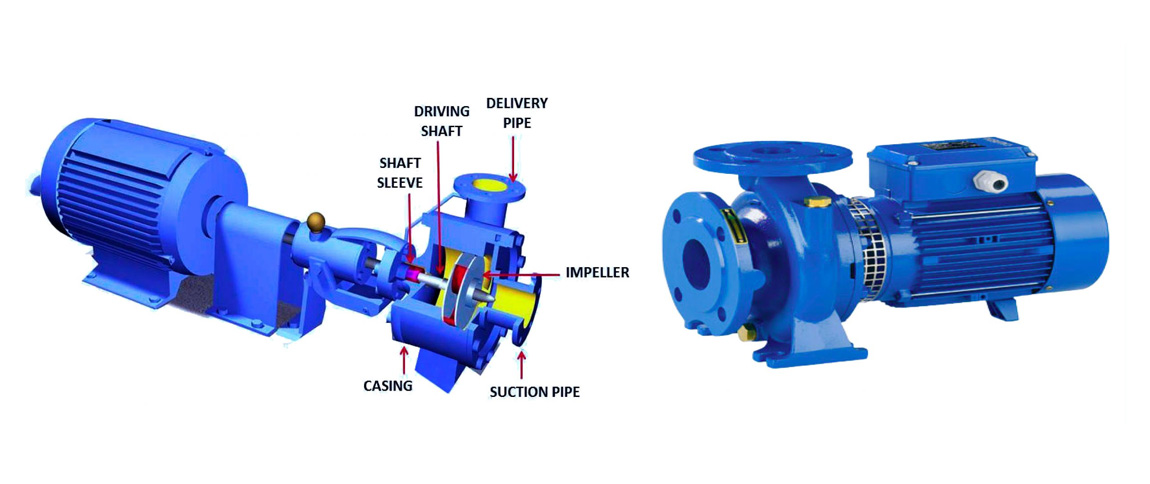
Single phase NEMA motors stand out as the leading solution for rugged workplaces in 2025. These motors offer unmatched reliability, durability, and efficiency, meeting strict NEMA standards for industrial performance. JOVAS Electric Motors, recognized among High-Efficiency Electric Motors Manufacturers, designs each single phase single phase nema motor with a heavy-duty steel frame and advanced capacitor start for high starting torque. The robust construction, IP44 protection, and low maintenance needs make these motors ideal for demanding environments. Consistent performance and compliance with efficiency regulations position the Nema Standard Motor and Induction Motor series as the smart choice for modern industries.
Key Takeaways
-
Single phase NEMA motors offer strong durability and high starting torque, making them ideal for tough industrial and commercial environments.
-
These motors use advanced designs like capacitor start and heavy steel frames to ensure reliable operation in dusty, wet, or harsh conditions.
-
NEMA premium efficiency standards help reduce energy use and lower costs, while supporting long motor life and stable performance.
-
Choosing the right motor size, enclosure type, and features like thermal overload protection improves efficiency and reduces maintenance needs.
-
JOVAS provides expert support and a wide range of motors that meet strict standards, helping users find the best fit for their rugged workplace needs.
Single Phase NEMA Motor Overview

Features
Single phase NEMA motors operate by applying a single alternating voltage to the stator winding. This process creates a rotating magnetic field at line frequency. To start the motor, a secondary coil with a capacitor generates a phase shift, which ensures the rotor turns in the correct direction. After startup, a centrifugal switch disconnects the starting circuit. These motors suit environments where a single-phase power supply is available.
JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD’s single phase single phase nema motor stands out due to its advanced engineering and robust construction. The heavy gauge steel frame and base provide exceptional strength. The capacitor start design delivers high starting torque, which is essential for heavy-duty machinery. Ball bearings guarantee smooth operation and long service life. The motor meets NEMA standards for universal design, including standardized dimensions and mounting options. Environmental adaptability allows operation in damp, dusty, or dirty conditions. The product line includes multiple frame sizes and housing options, such as aluminum and cast iron, to enhance durability and performance.
Tip: Choosing a single-phase ac motor with a 1.15 service factor helps tolerate temporary overloads, increasing reliability in demanding workplaces.
|
NEMA Class
|
Key Characteristics
|
Typical Industrial/Commercial Uses
|
|
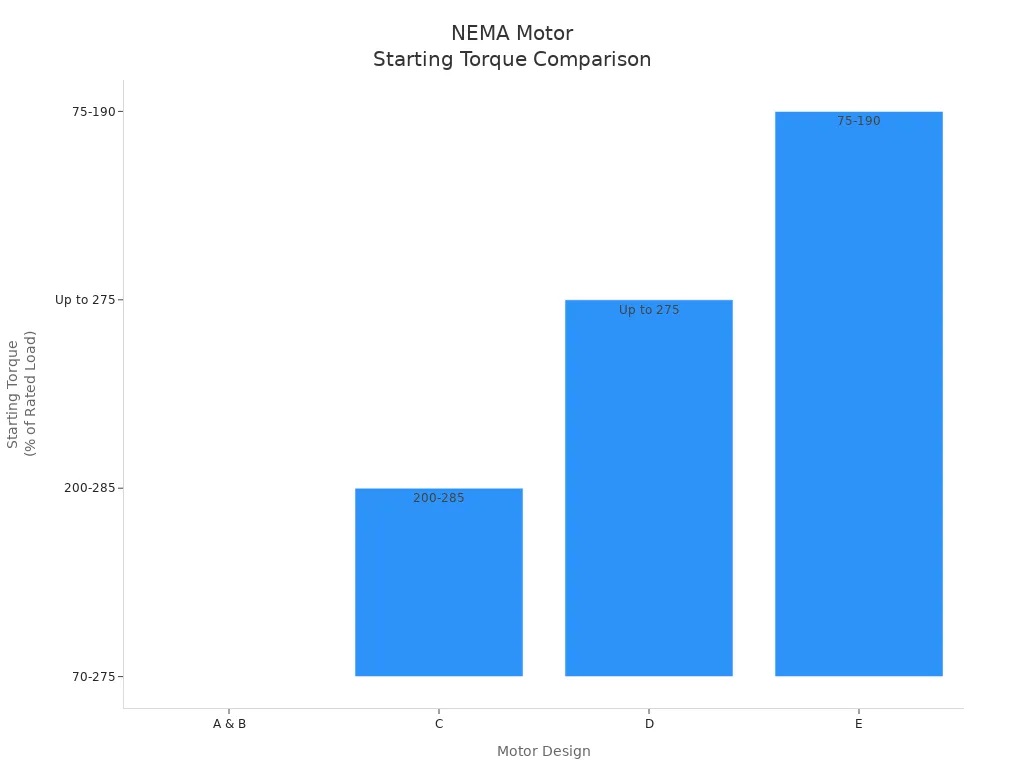
Class A
|
High breakdown torque, slip < 5%
|
Steady load industrial applications
|
|
Class B
|
General-purpose, slip 3-5% or less
|
Fans, pumps, blowers
|
|
Class C
|
High starting torque, normal current, low slip
|
Conveyors, compressors, heavy-duty machinery
|
|
Class D
|
Very high starting torque, high slip
|
Elevators, hoists, punch presses
|
|
Class E
|
High efficiency, low starting torque
|
Motor-generator sets, industrial blowers
|
Applications
Single phase single phase nema motor models from JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD serve a wide range of uses. These electric motors power compressors, pumps, fans, conveyors, and blowers. They perform reliably in environments with moisture, dust, or dirt. Industrial facilities use these motors for machinery that requires high starting torque and rugged reliability. Commercial buildings rely on single-phase ac motor units for ventilation and water systems. Residential settings benefit from their efficiency and low maintenance needs.
NEMA classifications help users select the right electric motors for specific tasks. The variety of single-phase ac motor designs, including capacitor start and asynchronous types, ensures compatibility with different operational requirements. Heavy-duty options meet the demands of challenging industrial applications. The efficiency of these motors supports energy-saving goals and reduces operational costs.
-
Single-phase motors receive one voltage waveform and include types such as shaded pole, permanent split capacitor, split phase, capacitor start/induction run, and capacitor start/capacitor run.
-
NEMA standards define frame sizes, horsepower ratings, service factors, and performance characteristics.
-
JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD offers motors designed for general purpose use in compressors, pumps, fans, conveyors, and blowers.
Benefits:
Reliability
NEMA single phase motors deliver outstanding reliability in rugged workplaces. Manufacturers design these motors with robust insulation systems, such as Class B and Class F, which allow higher operating temperatures and extend insulation life to over 20,000 hours. This design ensures continuous operation even in harsh conditions. JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD includes ball bearings and overload protection in their motors. These features help the motors operate smoothly and safely, even when exposed to demanding environments. Thermal overload protection shuts down the motor if it overheats, preventing damage and supporting long-term reliability. The motors maintain stable performance in high ambient temperatures, at altitude, or in areas with contamination. These qualities make NEMA motors a trusted choice for continuous operation in industrial settings.
Durability
Durability stands as a core advantage of NEMA motors. Heavy gauge steel frames and bases provide exceptional strength, allowing the motors to withstand physical impacts and vibration. The average lifespan of single phase NEMA motors in industrial settings ranges from 5 to 9 years for capacitor-start types, with some smaller models lasting up to 12 years. This long service life results from high-quality materials and careful engineering. Ball bearings, sealed for life, reduce the need for frequent lubrication and protect against moisture. The motors also feature enclosures that shield internal components from dust, dirt, and water. For example, totally enclosed water to air cooled (TEWAC) enclosures offer the highest protection, making these motors ideal for damp, dusty, or dirty environments. This rugged construction ensures that NEMA motors continue to perform where other motors might fail.
Efficiency
Efficiency plays a vital role in the performance of NEMA motors. JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD designs its motors to meet or exceed premium efficiency standards. These motors use optimized winding and capacitor configurations to achieve high efficiency and low starting current. The result is reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs. Premium efficiency motors also operate with less heat and vibration, which further extends their lifespan. Energy savings become significant over time, especially in continuous-use applications. The motors support energy efficiency goals in modern workplaces, helping companies meet regulatory requirements and reduce their environmental impact. High efficiency and motor efficiency combine to deliver both performance and cost benefits.
Note: Energy efficient motors not only lower electricity bills but also contribute to a greener workplace by reducing overall energy consumption.
|
Feature
|
Benefit
|
|
Premium efficiency
|
Lower energy use and operational costs
|
|
Motor efficiency
|
Less heat, longer life, and stable output
|
|
Energy savings
|
Reduced utility expenses and environmental impact
|
Low Maintenance
Low maintenance requirements set NEMA motors apart in demanding environments. The use of double-sealed ball bearings, which are lubricated for life, minimizes the need for regular servicing. Overload protection devices, such as manual reset thermal protectors, ensure that the motors shut down safely during extreme conditions. This reduces the risk of costly repairs and downtime. The simple structure of these motors, combined with robust construction, means fewer parts are likely to fail. Operators can rely on these motors for continuous operation with minimal intervention. The motors’ ability to perform in harsh conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, and contaminants, further reduces maintenance needs. This reliability translates into long-term savings and uninterrupted productivity.
Tip: Choosing NEMA motors with the right enclosure type ensures optimal performance and minimal maintenance in any workplace condition.
NEMA Premium Efficiency and Compliance:
Standards
NEMA premium efficiency standards set the benchmark for motor performance in 2025. These standards, including the latest ANSI/NEMA 10011:2024, use advanced testing methods that measure the efficiency of motors and their drive systems together. This approach gives a more accurate picture of real-world performance. The standards encourage manufacturers to design motors that deliver high efficiency under actual working conditions, not just in laboratory tests. By focusing on motor-drive combinations, the standards help users select motors that match their application needs and maximize energy savings.
The 2025 NEMA premium efficiency requirements push for higher efficiency levels, such as IE4 and IE5. These levels often require new technologies, like permanent magnet motors, which maintain efficiency across different loads. The standards also expand the range of motors that must comply, covering nearly all single-speed induction motors from 1 to 500 horsepower. This broad scope ensures that more workplaces benefit from energy savings and reduced operational costs. The coalition behind these standards projects up to 50 Quadrillion BTUs in energy savings by 2050, with $20 billion in consumer savings already achieved between 2022 and 2025.
Note: Enhanced NEMA premium efficiency standards make it easier for users to identify motors that offer the best energy efficiency and long-term savings.
Performance
JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD’s single phase NEMA motors meet or exceed NEMA premium efficiency standards. These motors comply with all key NEMA requirements for power, speed, and efficiency. The NEMA Premium® standard motors from JOVAS deliver high efficiency and reliability in a wide range of applications. Their design ensures stable operation in harsh environments, aligning with NEMA’s protection and operational guidelines.
-
JOVAS motors achieve premium efficiency by using optimized windings and advanced capacitor start designs.
-
The motors support energy efficiency goals, helping users reduce electricity costs and environmental impact.
-
Each motor is built to deliver consistent performance, even in demanding conditions.
-
The NEMA premium efficiency label on JOVAS motors assures users that these products meet or surpass the latest efficiency benchmarks.
-
Many JOVAS models reach above NEMA premium levels, offering even greater energy savings and operational benefits.
A focus on premium efficiency means that JOVAS motors help businesses achieve both immediate and long-term savings. Their commitment to enhanced NEMA premium standards ensures that every motor delivers reliable, high efficiency performance. Users can trust JOVAS motors to provide energy savings, durability, and compliance with all current and future regulations.
|
Feature
|
Benefit
|
|
NEMA premium efficiency rating
|
Lower energy use and cost savings
|
|
High efficiency design
|
Consistent performance and reliability
|
|
Above NEMA premium models
|
Maximum energy savings and compliance
|
|
Enhanced NEMA premium label
|
Easy identification of top efficiency
|
Applications in Rugged Workplaces

Industrial Use
Single phase nema motors play a vital role in many industrial settings. Companies rely on these motors to power compressors, pumps, fans, conveyors, and blowers. Market analysis shows that asynchronous motors dominate these sectors, driven by the need for energy efficiency and reliable operation. Industrial automation continues to increase demand for these motors. Manufacturers design nema motors to handle harsh conditions, such as dust, moisture, and vibration. Heavy-duty construction and high starting torque allow them to start and run large machinery with ease. The introduction of high-capacity models, like ABB’s AMI 5800 NEMA modular induction motor, highlights the focus on delivering robust performance for demanding applications. These motors support continuous operation, which is essential for production lines and processing plants. Their consistent performance and compliance with efficiency standards make them a preferred choice for rugged workplaces.
Note: Selecting the right nema motor ensures reliable operation and reduces downtime in industrial environments.
Household Appliances
Nema motors also show remarkable versatility in household and commercial appliances. They operate on single-phase power, making them suitable for residential and light commercial use. Their compact size and simple construction fit well in limited spaces. Many household appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and small pumps, use these motors. The motors provide quiet operation and low vibration, which is important for comfort in household settings. Manufacturers offer a range of power ratings, from 1/6 to 10 Hp, to match different appliance needs. Modern designs achieve high efficiency, helping reduce energy costs and environmental impact. Nema standards ensure compatibility and reliability across various appliances. The motors’ easy installation and off-the-shelf availability make them a practical choice for both new appliances and replacements.
Tip: Matching the motor’s specifications to the appliance ensures optimal performance and long service life.
Choosing the Right Motor:
Selection Tips
Selecting the right nema motor for a rugged workplace requires careful evaluation of several factors. Industry experts recommend starting with an assessment of the operating environment. Users should consider ambient temperature, moisture, dust, and contaminants. For example, open drip-proof (ODP) motors work well in clean, dry spaces, while totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed blower-cooled (TEBC) designs offer better protection in wet or dirty conditions.
A step-by-step approach helps ensure optimal performance and efficiency:
-
Assess the environment and select the appropriate motor construction type.
-
Confirm the available power supply and choose a single-phase or three-phase motor as needed.
-
Match the application with the correct nema motor type. ODP motors suit fans and pumps in clean areas, while TEFC or TEBC models excel in harsh environments.
-
Determine the correct motor size to prevent overheating and power loss.
-
Select features such as thermal overload protection and control options tailored to the system.
-
Follow installation guidelines, including proper mounting, wiring, and grounding.
-
Test and commission the motor to verify functionality.
-
Maintain documentation for future troubleshooting.
-
Schedule routine inspections to ensure ongoing efficiency and reliability.
Tip: Choosing the right enclosure type and motor size can significantly improve both efficiency and lifespan in demanding workplaces.
Support
JOVAS ELECTRICAL MACHINERY CO., LTD provides comprehensive support for customers selecting and operating single phase nema motors. Customers can reach out through multiple channels, including phone, email, WhatsApp, and live chat. The company offers technical assistance and product information to help users make informed decisions. Quick access to support ensures that any questions about installation, operation, or maintenance receive prompt attention. This level of service helps users maximize efficiency and reliability in their applications.